For laptops or desktop computers, Solid-State Drives (SSDs) and Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) are the two primary storage options available. Both serve the same purpose of storing data, but they differ significantly in terms of performance, design, and reliability. This article explores the key benefits of SSDs over HDDs and explains why SSDs are increasingly becoming the preferred choice for most users.
Contents
Advantages of SSD over HDD
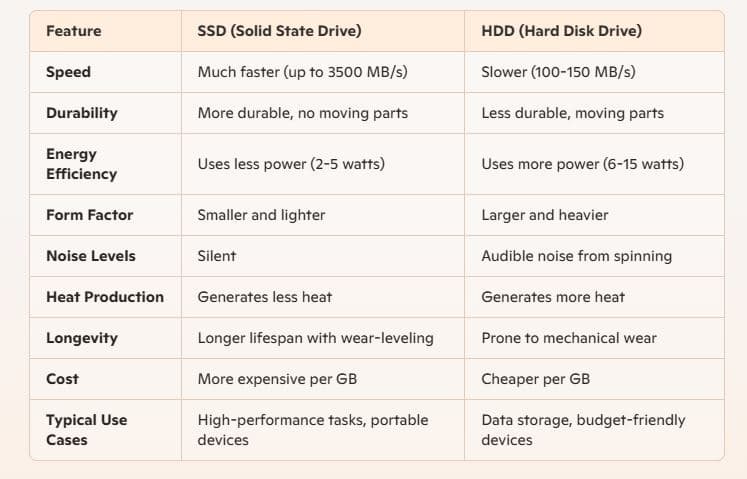
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) are traditional storage devices rely on spinning magnetic platters and mechanical arms to read and write data. In contrast, Solid-State Drive (SSD) represents a modern leap in technology, using NAND flash memory chips to store data electronically. While both HDDs and SSDs serve the same purpose of storing data, SSDs offer numerous advantages that make them a superior choice for many users. From faster speed and enhanced durability to better power efficiency and reduced noise, SSDs have redefined storage technology. Here are the key advantages SSDs offer over HDDs.
Faster Speed and Performance
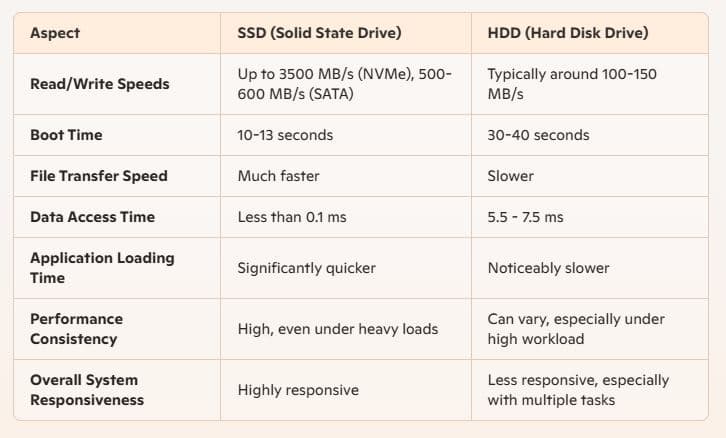
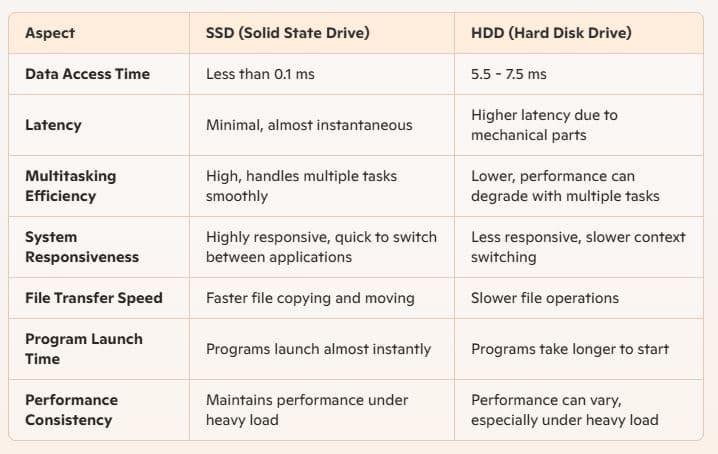
One of the most significant advantages of SSDs is their speed. SSDs use flash memory chips to store data electronically which allows for much faster read and write speeds compared to the mechanical components of HDDs. This means quicker boot times, faster file transfers, and a more responsive system overall. For tasks such as gaming, video editing, and running complex applications, SSDs provide a noticeable performance boost.
HDD can read/write data at speeds around 100-150 MB/s, an SSD can easily reach speeds of 500 MB/s or higher, with some NVMe SSDs read/write data speeds of up to 3500 MB/s.
SSDs offer shorter boot times for your computer, more immediate data transfer and higher bandwidth.
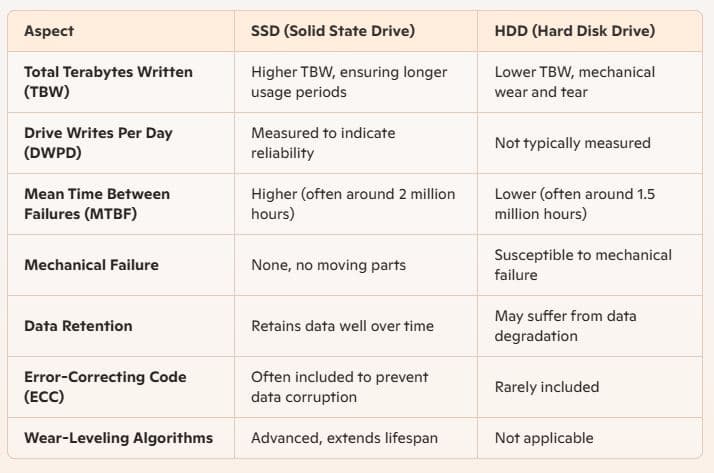
Durability and Reliability
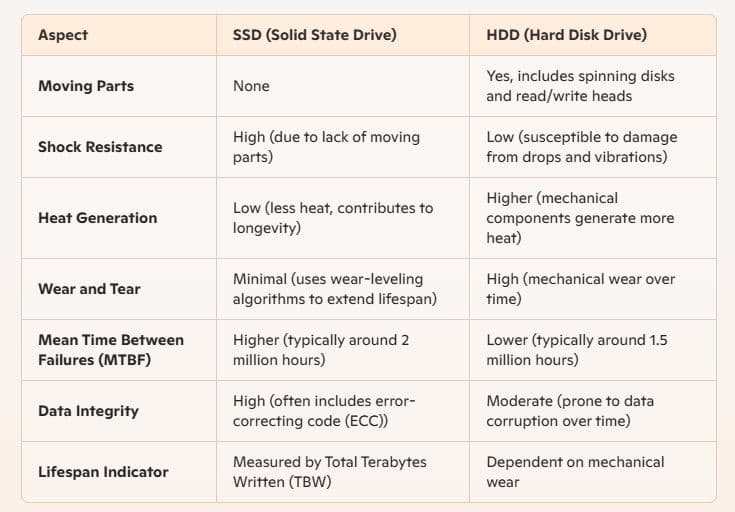
Heat is a major cause of failures in hard drives, and enough heat is generated by the continual motion of an HDD’s moving parts to cause it to break down over time. Since an SSD doesn’t have such parts, it can maintain a lower temperature with much higher performance.
Again HDDs rely on spinning disks and read/write heads, making them susceptible to damage from drops, bumps, and vibrations. SSDs, on the other hand, can withstand physical shocks and extreme conditions better, making them ideal for use in laptops and portable devices.
The average lifespan of an SSD is typically longer as well, often measured by Total Terabytes Written (TBW), which can be significantly higher compared to the number of read/write cycles of an HDD.
Energy Efficiency and Longer Battery Life
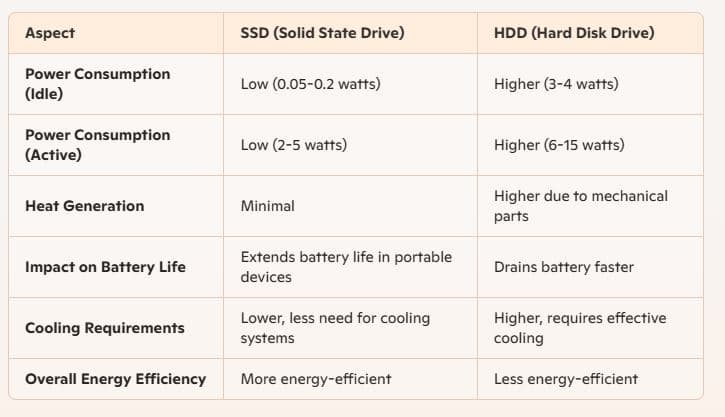
HDDs consume more power because their mechanical parts require continuous energy to operate. Where SSDs consume less power than HDDs because they don’t have to spin disks or move read/write heads. This lower power consumption translates to longer battery life for laptops and less heat generation, which can be beneficial for overall system longevity and performance.
For example, an HDD might use between 6-15 watts during operation, whereas an SSD generally uses between 2-5 watts. This difference can be especially important in battery-powered devices.
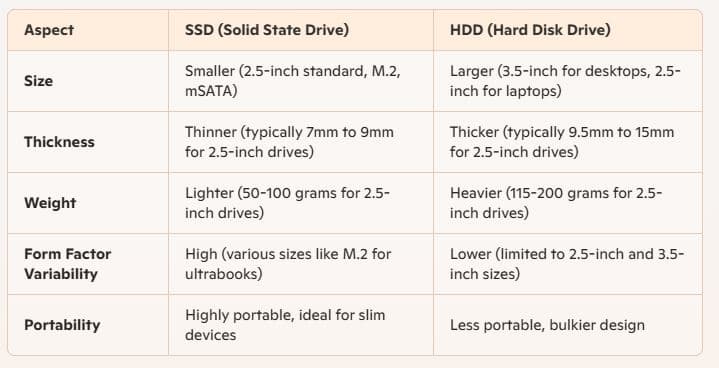
Form Factor and Weight
SSDs are typically smaller and lighter than HDDs, making them suitable for ultrabooks, tablets, and other compact devices. Their slim profile and light weight contribute to more portable and sleek designs, without compromising on storage capacity.
A standard 2.5-inch SSD weighs around 50-100 grams, whereas a similar capacity 2.5-inch HDD can weigh upwards of 115-200 grams. There are also even smaller M.2 and mSATA SSDs, which further reduce size and weight.
Silent Operation and Better Multitasking
The spinning platters and moving heads of HDDs produce noise during operation, especially under heavy workloads. Since SSDs don’t have moving parts, they operate silently. For users who prioritize a silent computing experience, SSDs are a clear choice.
Again HDDs struggle to handle simultaneous read and write operations due to their mechanical nature. However, SSDs offer seamless performance even when running multiple applications. This capability makes SSDs particularly valuable for professionals in video editing, programming, or gaming, where system responsiveness is critical.
Longer Lifespan and Advanced Features
HDDs wear out faster due to their moving parts, which are prone to mechanical failures after prolonged use. SSDs, with no such parts, have a longer lifespan in most scenarios. Modern SSDs use advanced wear-leveling algorithms to ensure even distribution of data writes across the memory cells, enhancing their lifespan. Additionally, many SSDs come with built-in error-correcting code (ECC) to prevent data corruption.
While HDDs might fail unexpectedly due to physical damage or motor breakdowns, SSDs are less likely to encounter such issues, offering greater peace of mind for long-term data storage.
Conclusion:
HDDs are more affordable and offer larger storage capacities, SSDs are best in speed, durability, energy efficiency, form factor, noise levels, heat production, and longevity.